Search engine optimization or SEO is the process of improving a website so that it appears higher in search engine results. Before moving to the topic let’s dig into the history of SEO, and how it started.
The first ever search engine was developed in 1990 named Archie. With a need to search the internet, many other search engines evolved later.
In 1995, Yahoo officially started its search engine services which was more like a directory listing websites of today.
Most of the searches were intended for information and navigation purposes. Later it moved for more commercial purposes and there started the need to optimize websites for higher ranking.
Early search engine algorithms used to rely upon keyword matching and webmasters used to stuff pages with keywords to rank higher.
Later in 1998, Larry Page and Sergey Brin founded Google. Google introduced PageRank, which started using backlinks instead of just keywords. The backlinks remain one of the largest ranking factors to date.
Unlike paid ads, SEO is free. Google has the largest share of the search engine market, (Around 90%). Forgive me if I write Google instead of search engine in the article 😀.
Why SEO?
Before we begin the topic, let’s understand why SEO remains the top choice for digital marketers, even after years of evolution, the rise of social media, and the explosive entry of AI?
SEO is sustained because SEO brings trust, sustainability, and unmatched ROI.
Social media is loud, flashy, and often short-lived.
Paid ads stop the moment you stop spending. But SEO? It builds organic visibility, brings high-intent traffic, and keeps delivering results long after the work is done.
It’s not just about ranking on Google. It’s about owning your audience’s attention when they’re actively looking for what you offer. In a digital world filled with noise, SEO is the signal. It’s not a trend. It’s a foundation.
SEO is not a marketing campaign, it’s an investment.
It’s not a steroid for quick gains; it’s a balanced diet and daily workout that builds lasting strength.
It’s not an allopathic pill, it’s Ayurvedic medicine, slow, steady, and healing from the core.
SEO Fundamentals
Let’s understand the basic fundamentals of SEO. How it works and how webmasters use this technique to achieve higher ranking.
SEO can be divided into four major parts.
- Keyword Research
- On-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
- Off-Page SEO
Let’s discuss these, one by one.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is finding the right words people are typing to find relevant information, products, or services.
Fortunately, we are in an age where we have enough data and trends on what exactly our target users are searching for.
If you are a beginner, you can start by guessing the words your target user is searching for. Once you have words or phrases, search for them in tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, etc.
The tools will help you with:
- Related keywords with volume.
- Keyword intent like informational, transactional, commercial, or navigational.
- Keyword difficulty or competition like how hard it is to rank.
- Trend analysis, if keyword is gaining or losing popularity. Also what time of year, a keyword is searched most or less?
Once you have a list of the right keywords, you can use them on the website with content.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is optimizing individual web pages to improve their rankings in search engines.
Google or any other search engine crawls the internet to find website pages, index them, and display them when anyone searches for relevant keywords.
Google processes over 8.5 billion searches per day and it indexes billions of web pages daily. So the question is how it decides which page to show for which query at a top?
To know how exactly Google search works, I recommend watching the 5 minutes video below:
Google has published an SEO Starter Guide for webmasters and keeps updating it from time to time.
Now let’s explore the On-page in depth.
Below are the key elements to optimize the On-page SEO process.
URL Structure
A well structured URL not only helps search engines to understand your page but also makes sense to users. If the URL is well structured with keywords, it helps in SEO too.
According to Kyle Roof, URL is one of the four magical places to put target keywords for the best possible chance of success with SEO. The other three will be discussed later in this article.
To create a SEO friendly URL structure, you need to keep three things in mind:
- Keep it short
- Make it readable
- Make it descriptive by adding keywords
- Add hyphen (-) instead of underscore (_)
- Avoid deep nesting e.g. example.com/products/vegetables/green-vegetables/leafy-vegetables/…
Good URL: example.com/green-leafy-vegetables
Bad URL: example.com/?page=41
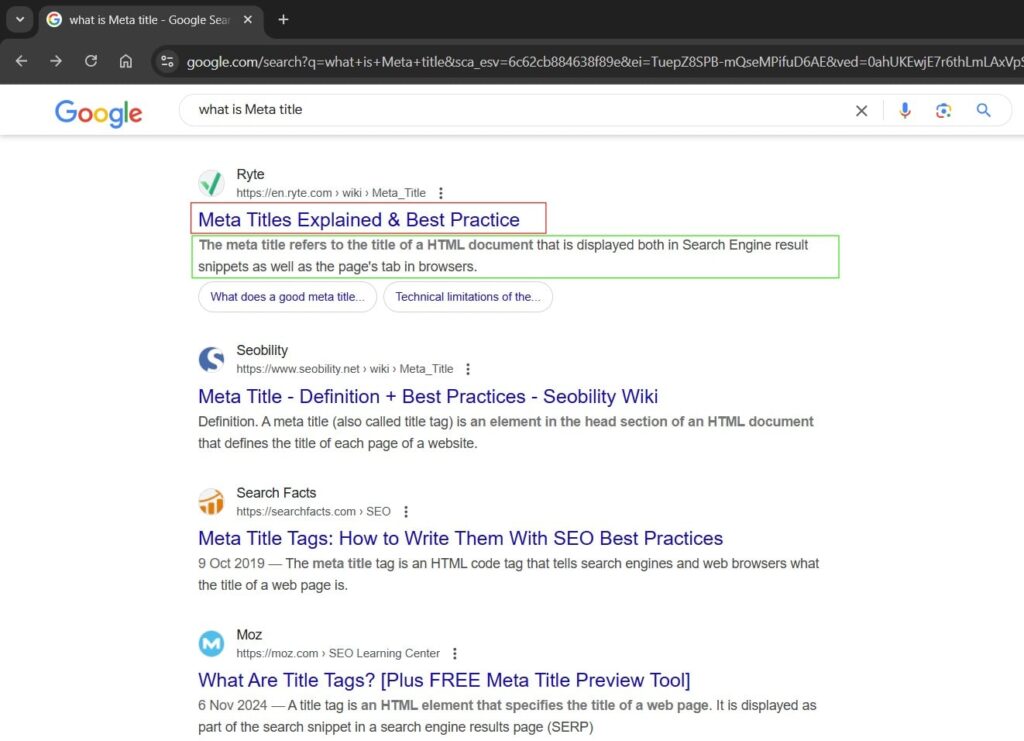
Meta Title
Meta title or title tag is an HTML tag that is defined each webpage. It appears in search engine results (SERP). This is Kyle Roof’s second magical place to put the target keyword.
Meta title has a big role in SEO ranking and Click Through Rate (CTR). It is one of the top ranking factors for SEO.
Just keep it under 60 characters and add keywords naturally. In the below screenshot, you can see the meta title marked in red that Google displayed in SERP.
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is also an HTML tag with a summary of a webpage’s content.
Google sometimes shows it below the page title and URL, helping users decide whether to click on the link.
Meta description is not a ranking factor but they significantly encourage users to click on a result and help SEO.
Headings
Headings not only improve readability and user experience but signal Google about the main topic of a page. The first heading of the page should be H1, which is Kyle Roof’s third magical place to put the target keyword.
Images
A picture is worth a thousand words. The quote is relevant in the SEO world too. Images enhance user experience and improve engagement, ultimately helping SEO.
You can add:
- Product pictures
- Infographic
- Feature image
- Screenshot
- User generated image
- Branded graphics
- Work in progress
Tips for image optimization:
- Use relevant descriptive keywords in the image. e.g. dentist-performing-teeth-whitening.jpg not img153100.jpg
- Don’t forget to add alt text
- Optimize file size by compressing the image
- Geotag self clicked images
- User ImageObject schema data
- Add Image Sitemap for better discoverability
- Use the right format for speed and quality e.g. WebP, jpg, SVG
- Use the lazy loading technique for better speed
Content
Content is the soul of the web page. Even if you did everything right and the page is ranking in Google, having not useful content will let the user leave the page. The first paragraph is Kyle Roof’s fourth magical place to put the target keyword.
Use clear headings, bullet points, and tables for better structure. Anticipates and answers all related user queries for in depth content. Run the readability test for a better user experience.
There is a lot of discussion over the length of content but there is no ideal length. The right length is the word count that could satisfy the user query.
Having in-depth content is always advisable. For In-depth content, include:
- Case studies
- Expert opinion
- Data and statics
- Quote examples and stories
- High quality images
- Infographics
- Link to useful resources
- FAQs
Build an authority around the topic. Google introduced EAT in 2014, which was an abbreviation of Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness. Later in 2022, google added one more ‘E’ for “Experience” making it EEAT. It’s a Google ranking factor and the future of content marketing.
Use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords to enhance SEO by improving content relevance. LSI keywords reduce keyword stuffing and help improve content comprehension for search engines.
Internal Linking
When creating content, we may need to reference various topics. However, it’s important to stay focused on the main subject of the page. For related topics, we can use internal or external links to provide additional information without straying from the core theme.
Internal links flow the link juice helping SEO. Adding external links could be helpful sometimes but add a nofollow attribute if you don’t want to pass link juice.
User Experience
User experience (UX) is at the core of effective SEO. From website speed and mobile responsiveness to content readability, structured navigation, and security, I have covered all the essential factors that contribute to a better user experience in SEO throughout this article. So need need to repeat them again.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about optimizing a website’s infrastructure. It covers the following topics of website SEO:
Crawling & Indexing
Search engines use bots to crawl web pages and index them in data centers in order to serve them in SERP. If a search engine bot is unable to crawl the website, it won’t index it. Any issues with crawling and indexing will void all your SEO efforts.
To make a website crawlable and indexable, just check out the list:
- Optimize robots.txt
- Add XML sitemap
- Add canonical tags
- Carefully use noindex and nofollow tags
- Internal linking for crawling and discovering and orphan pages
Website Speed and Performance
Website speed should be one of the top priorities for better user experience. check out the website speed optimization blog post for tips.
Work on improving Core Web Vitals which again is an SEO ranking factor. For those who don’t know what Core Web Vitals is, it’s a metric from Google that measures the three main elements:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): How fast is the largest visible content?
- FID (First Input Delay): Time taken for a page to respond after a user’s first interaction.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): How much the page layout shifts unexpectedly while loading.
Responsive Design
Being responsive is being responsible.
The way mobile and other small devices are surging, nobody can afford to ignore them. Check out our blog post on why websites should be responsive and how to make it responsive.
Once done, test the website on various screen sizes.
If you have a blog or other content type of website, you can go for AMP pages for better speed on mobile devices.
Website Security
Make sure your website uses a valid SSL certificate which is a ranking factor. Fix mixed content issues. Go for a reputed hosting and use CDN for better protection against hacking and attacks.
URL Structure and Broken Link Fixing
We already have discussed URL structure in the On-page section but along with individual pages, the entire website URL structure should follow clear navigation. Keep checking broken links reported in Google Search Console.
Structured Data Implementation
Help search engines understand your content better with schema markups. This could list you in rich snippets. Structured data will be a game changer in trending AI chatbots and voice search SEO.
Multilingual SEO
If you target multiple countries, use hreflang tag to present the right language and regional version of a page to search engines.
Off-Page SEO
As the name says, Off page SEO is optimization activities done outside of the website. In short, it’s about how your website is valued in the world of the internet. The value is calculated based on how much other websites recommend you. Each recommendation is a backlink, brand mentions, and social engagement.
Let’s understand each topic:
Backlinks
After Google introduced PageRank, links were added to the ranking factors list. Link works like votes for your website but unlike democracy, each vote has a different value.
For example, a link from RBI and a link from a financial advisor website has not same value. Gain quality backlinks form high authority relevant websites.
Below are the types of links you can create for backlinking.
- Editorial Backlinks
- Guest Posts
- Profile Creation
- Forum & Blog Comment
- Directory Submission
- Image & Infographic Submission
- Web 2.0 Backlinks
- And More…
Brand Mentions & Citations
Brand name mentioned even without a backlink can improve authority. Citations from local business directories can help local business SEO and website ranking.
Social Media Signals
In 2014, Matt Cutts, former Google head of web spam confirmed that social signals are not direct signals for search ranking. Again in 2020, John Mueller, a Google search advocate also repeated the same.
But does it mean, social media does not have an impact on ranking? They said “not direct signal” but it certainly increases user engagement, crawling, and brand awareness which contributes to better SEO.
Other
- PR marketing
- Influencer marketing
- Podcasts & webinars
- Reviews and testimonials
Need Help?
Do you own a business and looking for search engine optimization services? Nebula Infotech has over a decade of experience in digital marketing, especially SEO. We have a track record of achieving high competition keyword ranking. Contact us for a free SEO consultation.
I am Sunil Tarwara, a seasoned IT professional with over 13 years of hands-on experience in Website Development and Digital Marketing. With a deep understanding of the challenges faced by businesses, I have been trusted by hundreds of clients to achieve their digital goals. I have Master’s degree in Information Technology.
Apart from websites, I like hill stations.